







ASA Database Administration Guide
Connecting to a Database
Troubleshooting connections
In the next step towards establishing a connection, Adaptive Server Anywhere attempts to locate a server. If the connection parameter list includes a server name (EngineName (ENG) connection parameter), it carries out a search first for a local server (personal server or network server running on the same machine) of that name, followed by a search over a network. If no EngineName (ENG) connection parameter is supplied, Adaptive Server Anywhere looks for a default server.
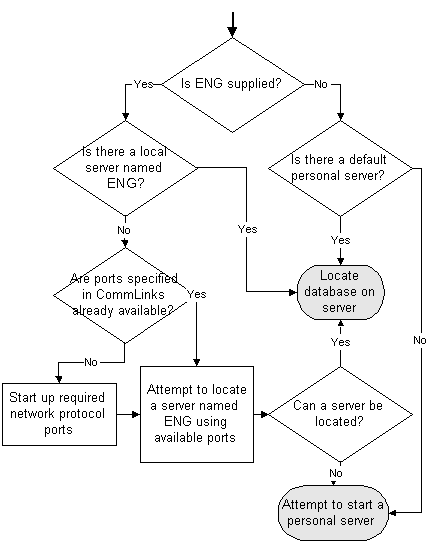
If Adaptive Server Anywhere locates a server, it tries to locate or load the required database on that server. For information, see Locating the database.
If Adaptive Server Anywhere cannot locate a server, it attempts to start a personal server. For information, see Starting a personal server.
For local connections, locating a server is simple. For connections over a network, you can use the CommLinks (LINKS) connection parameter to tune the search in many ways by supplying network communication parameters.
The network search involves a search over one or more of the protocols supported by Adaptive Server Anywhere. For each protocol, the network library starts a single port. All connections over that protocol at any one time use a single port.
You can specify a set of network communication parameters for each network port in the argument to the CommLinks (LINKS) connection parameter. Since these parameters are necessary only when the port first starts, the interface library ignores any connection parameters specified in the CommLinks (LINKS) connection parameter for a port already started.
Each attempt to locate a server (the local attempt and the attempt for each network port) involves two steps. First, Adaptive Server Anywhere looks in the server name cache to see if a server of that name is available. Second, it uses the available connection parameters to attempt a connection.



