







ASA Database Administration Guide
International Languages and Character Sets
Understanding character set translation
Error and other messages from the database software are held in a language resource library. Localized versions of this library are provided with localized versions of Adaptive Server Anywhere.
Client application users may see messages from the database as well as data from the database. Some database messages, which are strings from the language library, may include placeholders that are filled by characters from the database. For example, if you execute a query with a column that does not exist, the returned error message is:
Column column-name not found
where column-name is filled in from the database.
To present these kinds of information to the client application in a consistent manner, even if the database is in a different character set from the language library, the database server automatically translates the characters of the messages so that they match the character set used in the database collation.
To use character translation for database messages, ensure that the collation for your database is compatible with the character set used on your computer, and with the character set used in the Adaptive Server Anywhere language resource library. The language resource library differs among different localized versions of Adaptive Server Anywhere. You must check that the characters of interest to you exist in each character set.
Messages are always translated into the database collation character set, regardless of whether character set translation is turned on or off.
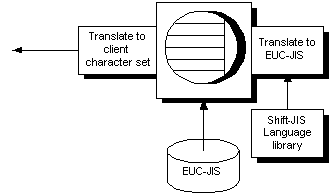
A further character set translation is carried out if character set is turned on (the default) for the database server, and if the client character set is different from that used in the database collation.



