




Introducing SQL Anywhere Studio
Replication Technologies
Propagation methods
SQL Remote exchanges data between databases using messages. Messages are typically files, placed in a particular directory, or specially formatted e-mail messages. A message agent, attached to each database, sends messages regarding changes to its own data. The same agent also receives messages from one or more other databases and modifies the database, according to the contents of the received messages. This system allows replication between databases that have no direct connection: an occasional message-based connection such as e-mail or a periodic dial-up link is sufficient.
In message-based communications, each message carries its destination address and other control information so that no direct connection is necessary between applications exchanging information. For example, an e-mail message contains the destination address; there is no direct connection between the sending server and the recipient.
Just as session-based client/server applications rely on network communication protocol stacks, such as TCP/IP or Novell NetWare's SPX, so message-based applications rely on message services such as Internet Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Microsoft's Messaging API (MAPI), Lotus' Vendor Independent Messaging (VIM), or a simple shared file link.
Message services use store-and-forward methods to get each message to its destination: for example, e-mail systems store messages until the recipient opens their mail folder to read their mail, at which time the e-mail system forwards the message.
Building a replication system on top of a message system means that a message-based replication system, such as SQL Remote, does not need to implement a store-and-forward system to get messages to their destination. Just as session-based client/server applications do not implement their own protocol stacks to pass information between client and server, so SQL Remote uses existing message systems to pass the messages.
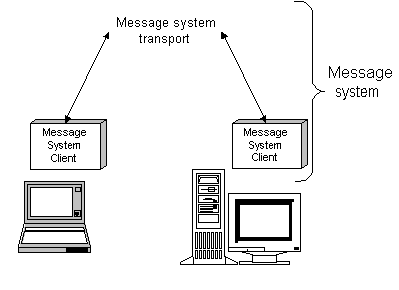
To work reliably, a message-based replication system must both guarantee that all messages reach their destination and that the messages are applied in the same order that they are sent. SQL Remote incorporates a protocol to guarantee application of replication updates in the correct order.



