







ASA SQL User's Guide
Accessing Remote Data
The following figure illustrates the remote Adaptive Server Anywhere tables employee and department in the sample database mapped to the local server named testasa.
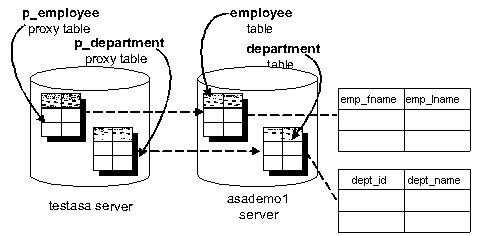
In real-world cases, you may use joins between tables on different Adaptive Server Anywhere databases. Here we describe a simple case using just one database to illustrate the principles.
To perform a join between two remote tables (SQL)
Create a new database named empty.db.
This database holds no data. We will use it only to define the remote objects, and access the sample database from it.
Start a database server running both empty.db and the sample database. You can do this using the following command line, executed from the installation directory:
dbeng9 asademo empty
Connect to empty.db from Interactive SQL using the user ID DBA and the password SQL.
In the new database, create a remote server named testasa. Its server class is asaodbc, and the connection information is 'ASA 9.0 Sample':
CREATE SERVER testasa CLASS 'asaodbc' USING 'ASA 9.0 Sample'
In this example, we use the same user ID and password on the remote database as on the local database, so no external logins are needed.
Define the employee proxy table:
CREATE EXISTING TABLE employee AT 'testasa..DBA.employee'
Define the department proxy table:
CREATE EXISTING TABLE department AT 'testasa..DBA.department'
Use the proxy tables in the SELECT statement to perform the join.
SELECT emp_fname, emp_lname, dept_name FROM employee JOIN department ON employee.dept_id = department.dept_id ORDER BY emp_lname



