Constructing Complex Shapes from Geometry Primitives
Constructive area geometry (CAG) is the process of creating new geometric shapes by performing boolean operations on existing ones. In the Java 2D™ API the
Area class implements the
Shape interface and supports the following boolean operations.
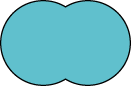 |
Union |
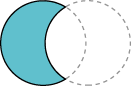 |
Subtraction |
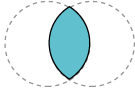 |
Intersection |
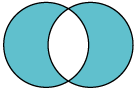 |
Exclusive-or (XOR) |
Example: Areas
In this example Area objects construct a pear shape from several ellipses.
Note:
If you don't see the applet running, you need to install release 6 (or later) of the Java SE Development Kit (JDK).
Pear.java contains the complete code for this applet.
The leaves are each created by performing an intersection on two overlapping circles.
leaf = new Ellipse2D.Double(); ... leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf2 = new Area(leaf); ... leaf.setFrame(ew-16, eh-29, 15.0, 15.0); leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf.setFrame(ew-14, eh-47, 30.0, 30.0); leaf2 = new Area(leaf); leaf1.intersect(leaf2); g2.fill(leaf1); ... leaf.setFrame(ew+1, eh-29, 15.0, 15.0); leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf2.intersect(leaf1); g2.fill(leaf2);
Overlapping circles are also used to construct the stem through a subtraction operation.
stem = new Ellipse2D.Double(); ... stem.setFrame(ew, eh-42, 40.0, 40.0); st1 = new Area(stem); stem.setFrame(ew+3, eh-47, 50.0, 50.0); st2 = new Area(stem); st1.subtract(st2); g2.fill(st1);
The body of the pear is constructed by performing a union operation on a circle and an oval.
circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(); oval = new Ellipse2D.Double(); circ = new Area(circle); ov = new Area(oval); ... circle.setFrame(ew-25, eh, 50.0, 50.0); oval.setFrame(ew-19, eh-20, 40.0, 70.0); circ = new Area(circle); ov = new Area(oval); circ.add(ov); g2.fill(circ);
