Finding and Loading Data Files
Whenever a Java applet needs to load data from a file that is specified with a relative URL (a URL that doesn't completely specify the file's location), the applet usually uses either the code base or the document base to form the complete URL.
The code base, returned by the JApplet getCodeBase method, is a URL that specifies the directory from which the applet's classes were loaded.
The document base, returned by the JApplet getDocumentBase method, specifies the directory of the HTML page that contains the applet.
Unless the <applet> tag specifies a code base, both the code base and document base refer to the same directory on the same server.
Data that the applet might need, or needs to rely on as a backup, is usually specified relative to the code base. Data that the applet developer specifies, often by using parameters, is usually specified relative to the document base.
Note:
For security reasons, browsers limit the URLs from which untrusted applets can read. For example, most browsers don't allow untrusted applets to use ".." to access directories above the code base or document base. Also, because untrusted applets cannot read files except for those files on the applet's originating host, the document base is generally not useful if the document and the untrusted applet reside on different servers.
The JApplet class defines convenient forms of image-loading and sound-loading methods that enable you to specify images and sounds relative to a base URL. For example, assume an applet is set up with one of the directory structures shown in the following figure.
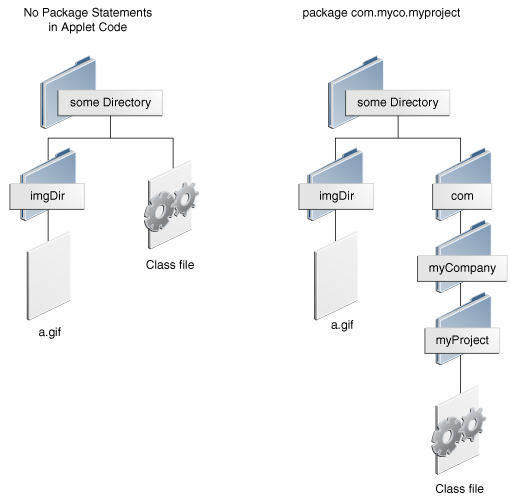
To create an Image object that uses the a.gif image file under imgDir, the applet can use the following code:
Image image = getImage(getCodeBase(), "imgDir/a.gif");
