







MobiLink Synchronization User's Guide
Transport-Layer Security
A deployment of MobiLink that involves multiple servers can be improved by assigning each server a unique certificate also signed by a common root certificate. A certificate authority within the enterprise holds the root certificate.
This arrangement has the following advantages:
Each MobiLink synchronization server can be given a unique certificate, so that if one site is compromised, the others are not affected.
Security is enhanced because the private key for the enterprise root certificate need not be stored on the MobiLink synchronization server.
Clients do not need to keep a copy of each server's public certificate, only a copy of the public root certificate because you can configure them to trust any certificate signed by the root certificate.
The security of the system can be improved somewhat by obtaining a globally signed certificate, discussed later, from a commercial certificate authority. In practice, however, this arrangement provides adequate security for many applications.
You can program your clients to verify the values of some certificate fields, as discussed later. In this way, you can ensure that your clients synchronize with particular MobiLink synchronization servers within your organization.
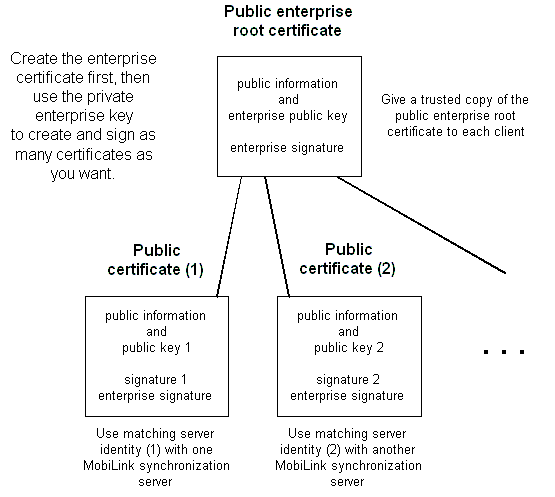
This setup provides more flexibility than self-signed server certificates. For example, you can add a new server and give it a new certificate. If the new certificate is signed with the same enterprise root certificate, existing clients will automatically trust it. Were you, instead, to give each MobiLink synchronization server a self-signed certificate, all clients would require a copy of the new public certificate.
Creating the certificates
Using the signed certificates



