On Win32 platforms, JavaTM Plug-In software is bundled with
the Java 2 Runtime Environment. Java Plug-In lets web browsers
use the Java 2 Runtime Environment to run 1.2-based applets and
JavaBeansTM components instead of the web browser's default
virtual machine. The Java Plug-In works with Netscape Communicator
and Microsoft Internet Explorer.
Get Downloads
To install and use the Java Runtime Environment with Java Plug-In,
you need the following downloads. Put the downloads in a temporary
directory.
- Java Runtime Environment with Java Plug-In for Win32 Platforms.
- Java Plug-In HTML Converter
Install JRE with Java Plug-In
An optionally installable version of the Java 2 Runtime Environment with
Java Plug-In is included with the
Java 2 SDK
download. You can also download and install Java 2 Runtime Environment with Java Plug-In
separately.
Either way, install the Java 2 Runtime Environment with
Java Plug-In by double-clicking its icon and following the
installation instructions.
When the installation completes, you will see the Java Plug-In
control panel on your Windows Start menu under
Programs.
Install the HTML Converter
Your browser will not automatically use the
Java Plug-In when you load an HTML file with an applet.
You have to download and run the Java Plug-In HTML Converter
on the HTML page that invokes the applet to direct
the applet ro run using the
plug-in instead of the browser's default runtime.
Unzip the Java Plug-In HTML Converter download:
unzip htmlconv12.zip
Add the HTMLConverter.java program or its
directory to your CLASSPATH.
Security Policy File
The auction application uses an applet running in a browser for administrative
operations. In the JavaTM 2 platform, applets are restricted to a
sandbox-like environment and need permission to access system resources
outside their restricted environment. Applets are restricted to read
operations within their local directory. All other access operations
require permission.
Types of Policy Files
You need a policy file to grant access permissions to the
Administration applet. If the applet runs on a disk other
than the disk where the browser is running, the applet will
also need to be signed. See
Signed Applets for information
on signing and deploying applets.
There are three kinds of policy files:
system, user, and program.
The system policy file is located in
jdk1.2\jre\lib\security\java.policy or
jre1.2\lib\security/java.policy and contains
permissions for everyone on the system.
The user policy file is located in the user's home directory.
The user policy file provides a way to give certain users
additional permissions over those granted to everyone on
the system. The permissions in the system file are combined with
the permissions in the user file.
A program policy file can be located anywhere. It is
specifically named when an application is invoked
with the java command or when an applet
is invoked with applet viewer. When an application or
applet is invoked with a specific policy file, the permissions
in that policy file take the place of (are not combined with)
permissions specified in the system or user policy file.
Program policy files are used for program testing or
intranet deployment of applets and applications.
Install the Security Policy File
Place the security policy file in your home directory and name
it java.policy. When the applet tries to perform an action that
requires a policy file with a permission, the policy file is loaded from this
directory and remains in effect until you exit and restart the browser.
If an applet tries to perform an access operation without the right
permission, it quietly quits without raising either an applet or
a browser error.
Changing the Name or Location
You can change the name and/or location of the default system or
user policy file. Edit the jdk1.2\jre\lib\security\java.security
or jre1.2\lib\security\java.security
file and add a third entry specifying the name and location
of an alternative policy file.
policy.url.1=file:${java.home}\lib\security\java.policy
policy.url.2=file:${user.home}\java.policy
policy.url.3=file:\<mypolicyfile path and name>
Note: On Windows/NT machines, you might
place the policy file in the
C:\Winnt\Profiles\<userid>\java.policy
directory.
Run the Administration Applet
Copy the Java Archive (JAR) file with the Administration
applet and policy file to its final location. In this
example, that location is the \home\zelda\public_html
directory. Next, extract the applet class file and policy file
from the JAR file:
cp admin.jar \home\zelda\public_html
jar xf applet.jar
The extraction places the policy file under public_html
and creates an admin directory under
the public_html directory with the
applet class file in it. Rename the policy file in the
public_html directory to
java.policy and copy it to your home directory.
In the public_html directory, create an HTML file that invokes
the Administration applet class. Be sure to include the admin
directory when you specify the applet class to the CODE option.
Note that when using Java Plug-In, you cannot have the browser
load the class file from the Java Archive (JAR) file.
<HTML>
<BODY>
<APPLET CODE=admin/AdminApplet.class
WIDTH=550
HEIGHT=150>
</APPLET>
</BODY>
</HTML>
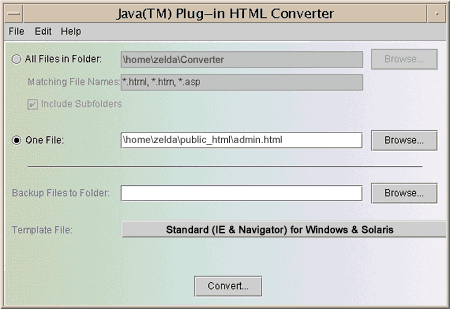
Start the HTML Converter.
java HTMLConverter
In the HTML Converter graphical user interface, select One File:,
specify the path to the admin.html file,
and click the Convert button.
How Does It Work?
On Windows machines, the Java Plug-In finds the Java Runtime
Environment (JRE) by running the OLE custom control file
beans.ocx installed by default in the
\Program Files\JavaSoft\1.2\bin web browser directory.
The OLE control examines the Windows registry to find the Java Plug-In
key and uses the value associated with that key to find the installed JRE.
If you find that the wrong JRE is being loaded, use regedit
to check the Java Plug-In registry values for the current user. If no JRE
is installed, the control checks the Java Plug-in values for
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE. You should see a value for Java Runtime
Environment under Software\JavaSoft.
After the conversion completes, load the admin.html file in your browser.
[TOP]


