
Java EE Containers
Normally, thin-client multitiered applications are hard to write because they involve many lines of intricate code to handle transaction and state management, multithreading, resource pooling, and other complex low-level details. The component-based and platform-independent Java EE architecture makes Java EE applications easy to write because business logic is organized into reusable components. In addition, the Java EE server provides underlying services in the form of a container for every component type. Because you do not have to develop these services yourself, you are free to concentrate on solving the business problem at hand.
Container Services
Containers are the interface between a component and the low-level platform-specific functionality that supports the component. Before a web, enterprise bean, or application client component can be executed, it must be assembled into a Java EE module and deployed into its container.
The assembly process involves specifying container settings for each component in the Java EE application and for the Java EE application itself. Container settings customize the underlying support provided by the Java EE server, including services such as security, transaction management, Java Naming and Directory Interface
(JNDI) lookups, and remote connectivity. Here are some of the highlights:
- The Java EE security model lets you configure a web component or enterprise bean so that system resources are accessed only by authorized users.
- The Java EE transaction model lets you specify relationships among methods that make up a single transaction so that all methods in one transaction are treated as a single unit.
- JNDI lookup services provide a unified interface to multiple naming and directory services in the enterprise so that application components can access these services.
- The Java EE remote connectivity model manages low-level communications between clients and enterprise beans. After an enterprise bean is created, a client invokes methods on it as if it were in the same virtual machine.
Because the Java EE architecture provides configurable services, application components within the same Java EE application can behave differently based on where they are deployed. For example, an enterprise bean can have security settings that allow it a certain level of access to database data in one production environment and another level of database access in another production environment.
The container also manages nonconfigurable services such as enterprise bean and servlet life cycles, database connection resource pooling, data persistence, and access to the Java EE platform APIs (see section Java EE 5 APIs).
Container Types
The deployment process installs Java EE application components in the Java EE containers illustrated in Figure 1-5.
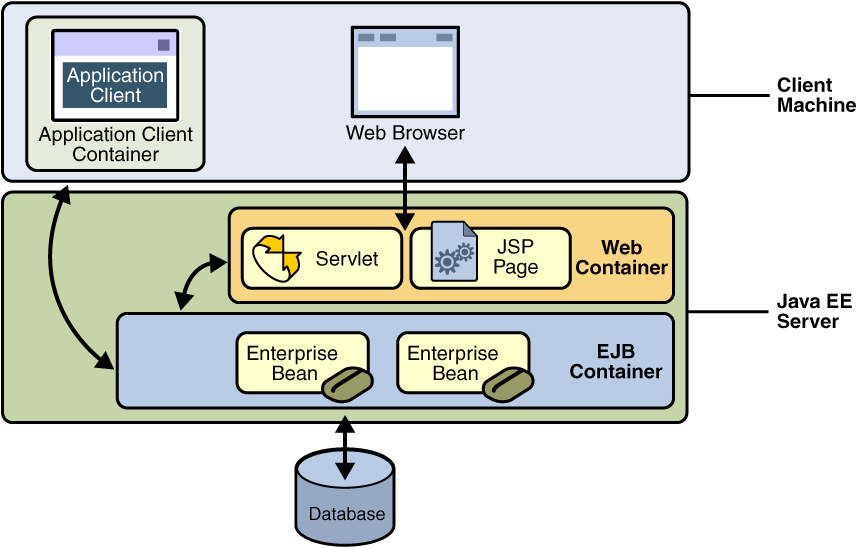
Figure 1-5 Java EE Server and Containers
Java EE server
The runtime portion of a Java EE product. A Java EE server provides EJB and web containers.
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) container
Manages the execution of enterprise beans for Java EE applications. Enterprise beans and their container run on the Java EE server.
Web container
Manages the execution of JSP page and servlet components for Java EE applications. Web components and their container run on the Java EE server.
Application client container
Manages the execution of application client components. Application clients and their container run on the client.
Applet container
Manages the execution of applets. Consists of a web browser and Java Plug-in running on the client together.